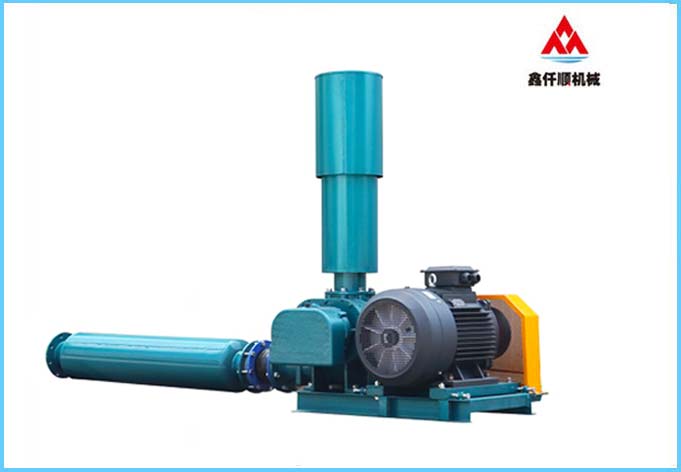
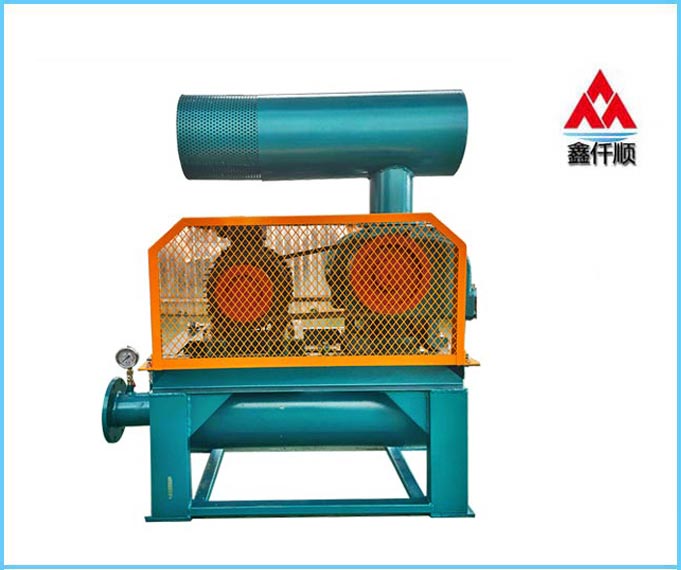
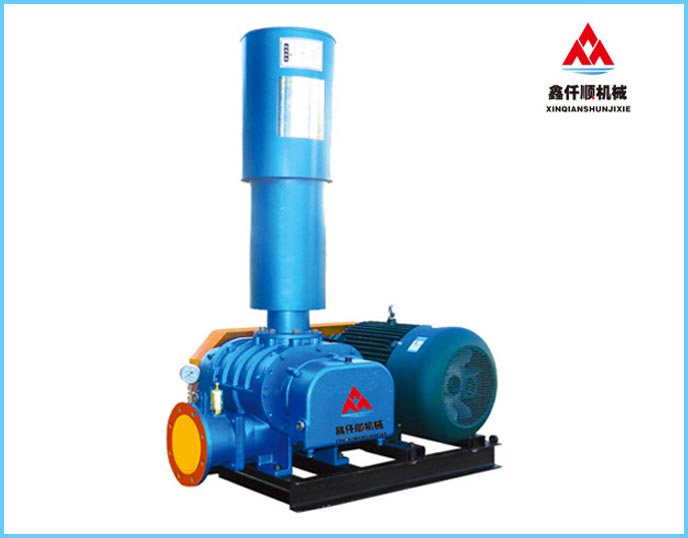
Roots blower, English name is Roots blower, which is a rotary compressor that uses two blade rotors to make relative movement in the cylinder to compress and transport gas. The blower has simple structure and is easy to manufacture. It is suitable for gas transmission and pressurization at low pressure occasions, and can also be used as a vacuum pump.
Roots blower It belongs to volume rotary blower. The compressor keeps the two rotors engaged by the synchronous gear at the rotor shaft end. Each concave curved surface on the rotor forms a working volume with the inner wall of the cylinder. During the rotation of the rotor, the gas is taken away from the suction port. When the rotor moves to the exhaust port near which it is connected with the exhaust port, the pressure in the working volume suddenly rises due to the backflow of high pressure gas, and then the gas is transported to the exhaust channel. The two rotors do not contact each other, and they are sealed by a tightly controlled gap, so the discharged gas is not polluted by lubricating oil.
Its biggest feature is that when the pressure is adjusted within the allowable range, the flow changes little, the pressure selection range is wide, and it has the characteristics of forced gas transmission. The medium does not contain oil during transportation. Simple structure, convenient maintenance, long service life and low vibration of the whole machine.
Vacuum pump. The periodic suction, exhaust and instantaneous constant volume compression cause the pulsation of gas flow velocity and pressure, which will produce large aerodynamic noise. In addition, the clearance between rotors and between rotors and cylinders will cause gas leakage, thus reducing efficiency. The exhaust volume of Roots blower is 0.15~150 m3/min, and the rotating speed is 150~3000 rpm. The single stage pressure ratio is usually less than 1.7, up to 2.1, and can be used in series.

The transmission medium of Roots blower is clean air, clean gas, sulfur dioxide and other inert gases, the preferred products for special gas industry (gas, natural gas, biogas, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, etc.) and high-pressure working conditions. In view of the above characteristics, it can be widely used in metallurgy, chemical industry, fertilizer, petrochemical, instrument and building materials industries. According to the shape of rotor, Roots blower is divided into two blade type and three blade type. The three blade rotor is sucked and exhausted three times by two rotors every time it rotates. Compared with the two blade type, the gas pulsation is small, the vibration is small, and the noise is low. The speed of Roots blower is 150~3000 rpm. The flow is 0.15~1200 m3/min, the pressure is 9.8~196 kPa, the power is 0.75~1000 kW, and the unit weight is 100~9000 kg.
It is quite different from centrifugal fan:
1. The working principle is different. The centrifugal fan uses curved blades to throw the gas to the casing by centrifugal force, while the Roots fan uses two 8-shaped blades with a small gap between them. The gas is squeezed to the air outlet by the extrusion of the two blades.
2. Due to different working principles, their working pressures are generally different. The outlet pressure of Roots blower is relatively high, while that of centrifugal blower is relatively small.
3. The air volume is different. Generally, Roots blower is used in places with low air volume requirements but high pressure requirements, while centrifugal blower is used in places with low pressure requirements and high air volume requirements.
4. The manufacturing precision is different. Roots blower requires high precision and strict assembly requirements, while centrifugal blower is relatively loose.
Operation adjustment
According to the theory of fluid mechanics, the flow process of gas will be accompanied by loss. For example, after the gas flows through the throttling device, the pressure of the gas flow will be reduced accordingly, that is, they will lose the useful work of the fan. Because all this happens in the process of the fan conveying gas, it wastes the energy of the fan.
The operating point of fan is the intersection of the performance curve of fan at a certain speed and the resistance characteristic line of pipe network. The actual operation of the fan does not always stay at the design operating point. It will change with the user's demand or the change of external conditions, that is, the fan actually works under variable conditions. In order to make the air pressure or air volume of the fan reach a certain target value, it is necessary to artificially control the fan or pipe network, also known as regulation. Through effective regulation, it can not only meet the requirements of production on flow or pressure, but also maximize energy saving under the condition that the fan can work stably. In short, the purpose of regulation is to meet performance requirements, expand (stabilize) working conditions, achieve energy conservation and prevent surge.
Different adjustment modes of fans can achieve the same purpose, but the energy-saving effect is different. According to theoretical analysis and practical proof, the following four conclusions can be drawn.
(1) For the blower and compressor, the outlet throttling mode consumes the most power. Although the relative flow Qr (the ratio of actual flow Q to design flow Q0) decreases, the power also decreases accordingly. For example, when Q=0.65 Q0, the corresponding power is reduced to about 80% of the original, but compared with other adjustment methods, the energy consumption still ranks first.
⑵ If the relative flow changes little (or the regulating depth is small), the power consumption of several regulating methods is not different. That is to say, the regulation mode has little impact on the energy saving effect, even does not save energy, but consumes more power due to the existence of the regulation device (such as hydraulic coupler).
⑶ Generally speaking, the greater the adjustment depth, the more significant the energy-saving effect. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully select the adjustment mode in order to obtain the maximum benefit.
⑷ The speed change adjustment curve is close to the ideal curve. Therefore, the variable speed regulation mode is superior, especially the energy-saving scheme of variable frequency motor speed regulation is the best, but it needs to add a variable frequency device. For medium and small capacity frequency conversion speed regulation, it is recommended to actively try; Due to the high price of high-capacity and high-voltage variable frequency speed regulation device, it is necessary to make a comprehensive comparison and decide whether to accept or reject it according to the specific situation. In a word, it is necessary to consider not only the regulation performance, but also the initial investment, reliability and economy of equipment, and comprehensively evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of the regulation mode.