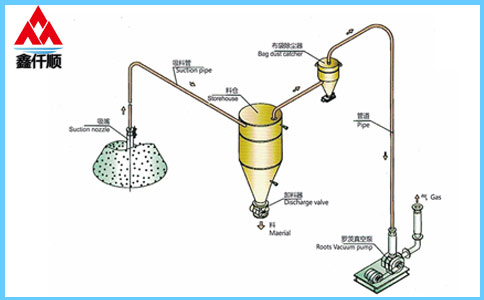
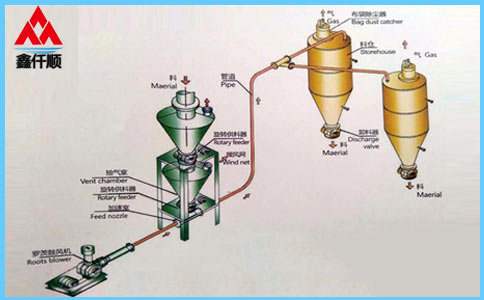
What are the selection methods of Roots blower? Determination of working condition parameters of Roots blower:
As a prerequisite for selecting roots blower, the system requirements for flow and pressure rise of roots blower shall be determined by calculation or analogy.
1. Calculation method
(1) Flow. In order to meet the needs of development, a certain amount of spare capacity is usually reserved when designing process systems. When selecting the blower, the flow of the blower shall be determined according to the capacity required by the system design to match the capacity of other equipment in the system. Considering the influence of air leakage loss, the flow should have a certain margin, and the flow of the blower is generally 1.1~1.25 times of the flow required by the system. In addition, if the flow rate changes during the production process, the flow rate given in the process has three values: normal, minimum and maximum. The maximum flow rate shall be taken as the basis for model selection.
(2) Boost. As a forced blower, the pressure rise of Roots blower is always balanced with the pressure drop of the system. Considering the complexity of the pressure drop calculation in the process design, for the sake of conservatism, certain margin should be left when determining the pressure rise of the blower, which is generally 1.05~1.15 times of the system pressure drop. If the system pressure drop changes frequently during production, the pressure rise of the blower must be determined based on the maximum pressure drop.
2. Analogy
It is also a common method to determine the working condition parameters of the blower by referring to the configuration of existing similar systems, or by analogy and calculation according to similar devices.
Selection of Roots blower model:
1. Model of Roots blower
There are two categories of aircraft types: broad and narrow. In a broad sense, the model refers to the structural type of the blower. In a narrow sense, model refers to specific product models and performance specifications. Among them, the model is a group of codes reflecting the structural characteristics of the product, and the performance specification mainly refers to the flow and pressure of the blower.
2. Model selection
There is often more than one type of blower that can meet the flow and pressure requirements for one purpose. The principle of choice is one of applicability and the other is economy. From the perspective of applicability, besides the pressure and flow must meet the requirements, the reliability of product use, such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance and sealing performance, should also be considered. From the perspective of economy, among the various models available, the selection should be based on the requirements of high efficiency, energy saving, high quality and low price, or focus on one of them.
For the same flow, the smaller model can be used to achieve the flow at a higher speed, or the larger model can be used to meet the flow at a lower speed. The former is small in size, light in weight and high in efficiency, but has adverse effects on vibration, noise and service life; The latter features smooth operation, low noise, long service life, large volume and weight, and relatively high cost. If economic considerations are emphasized, small models with high speed can be selected; If the stability is emphasized, large models with low speed can be selected.
For the same performance requirements, either direct coupled transmission or belt coupled transmission can be selected; It can be either a dense complete set of units or a common group. Generally speaking, direct transmission should be preferred when conveying flammable and explosive gases. If belt transmission is used, anti-static belt must be used. Belt coupling transmission can be selected when conveying dusty gas. Even if the rotor clearance increases due to dust wear, the flow can be adjusted within a certain range by replacing the pulley. In the sense of simple type selection and installation, it is better to select dense complete sets of units, but for the sake of convenient maintenance, ordinary group mode is still used in most occasions.
For specific pressure and flow, the products of several manufacturers may meet the requirements. However, the product quality, sales price and service level may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. In terms of product quality, in addition to the two indicators of flow and pressure, there are also shaft power (or specific power), product manufacturing accuracy (such as synchronous gear accuracy), sealing performance, noise value, etc. When selecting a model, a comprehensive comparison of various factors should be made. Under the condition of reasonable price, it is better to choose products with good quality and high efficiency. Relatively speaking, they have lower operating costs, higher output benefits and longer service life.
3. Material selection
Conventional products are designed to deliver air. Therefore, when used as an air blower, it is generally unnecessary to consider the material problem. However, except for air, some gases should not be in contact with some materials, and the material characteristics of parts should be taken into consideration when selecting.
For example, when transporting nitrogen, the parts in contact with it should not use copper materials. When transporting oxygen and chlorine, the parts in contact with it should not be made of aluminum alloy materials. When transporting hydrogen, sulfur dioxide and acetylene, the parts in contact with them should not use aluminum alloy materials and copper materials. When transporting wet hydrogen chloride, carbon steel, aluminum alloy and copper materials should not be used for the parts in contact with it. When transporting wet hydrogen sulfide, carbon steel, gray cast iron and copper materials should not be used for the parts in contact with it.
In some cases, the main gas flow may not be corrosive, but the influence of impurities cannot be ignored. For example, transportation of dry pure chlorine and transportation of chlorine containing 5% water are quite different; Copper materials can be used to transport dry carbon dioxide, but not wet carbon dioxide.
Sometimes, it is not a problem to select the main parts according to the conventional materials, but the influence of some minor factors cannot be ignored. For example, when conveying acetylene, the impeller, casing, wallboard and other main parts can still be made of cast iron, but the bearing cannot use copper and aluminum cages as usual (unless it does not contact acetylene).
4. Selection of sealing type
The seal type of the blower includes labyrinth seal, expansion ring seal, packing seal, mechanical seal and skeleton oil seal group. Generally speaking, different seal types have different sealing effects and different applicable characteristics. For different media, especially flammable, explosive, toxic, corrosive gases and rare and valuable gases, the sealing type must be reasonably selected according to the principle of effective sealing and economic practicality.
The air blower for conveying air is not too restrictive to the external leakage, so labyrinth seal can be selected. If the packing seal, expansion ring seal or mechanical seal is selected, the manufacturing cost is high, and the maintenance and repair are also troublesome, which is not economical.
For the blower with nitrogen as the medium for pneumatic conveying, in order to prevent the leakage of powder particles through the shaft end clearance, or prevent the air from mixing into the conveying system, the sealing type of "closed wallboard ● inflatable labyrinth" can be selected. At this time, a set of gas filled labyrinths are set at each of the four shaft ends. When working, nitrogen with high pressure is charged into the middle section of the labyrinth, and the inner cavity of the wallboard is connected with the nitrogen recovery system.
The gas blower conveying gas is not allowed to enter the lubrication system, otherwise it will dilute the lubricating oil (or grease). The sealing type of "open wallboard ● packing seal" can be selected. A group of packing seals are set at each of the four shaft ends to completely isolate the medium in the casing from the gear, bearing and its lubrication system.
For the blower conveying sulfur dioxide and gas, the seal type of "open wallboard ● comb labyrinth" or "open wallboard ● skeleton oil seal group" can be selected, and one set of comb labyrinth or skeleton oil seal group can be set at each of the four shaft ends. When using the comb labyrinth, the air leaked into the labyrinth can be led back to the air inlet of the blower by using the air extraction pipe.
When transporting helium, argon and other rare gases as well as methane, hydrogen and other flammable and explosive gases, in order to control their external leakage, the seal type of "closed wallboard ● single mechanical seal" can be selected, and a group of mechanical seals can be set at the shaft extension.
When transporting acetylene and liquefied petroleum gas, in order to control their external leakage, the sealing type of "closed wallboard and four mechanical seals" can be selected. A group of mechanical seals are set at the tail of four bearing seats, and the mechanical seals are lubricated and cooled with the help of bearing lubricating oil.
When transporting oil proof media such as oxygen, the seal type of "open wallboard and four mechanical seals" can be selected. One set of mechanical seals is set at each of the four shaft ends to ensure that the lubricating oil of bearings and gears does not enter the casing.
6KV high-voltage roots blower
Selection of Roots blower motor:
1. Selection of motor type
There are many types of motors. The blower is generally equipped with three-phase squirrel cage asynchronous motor, which can be divided into the following situations according to the service environment:
(1) For indoor use, Y series, JS series and other general purpose three-phase asynchronous motors can be selected, of which Y series are energy-saving products promoted by the country.
(2) For products used outdoors by petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical and other departments, as well as places with certain corrosive media in the indoor environment, Y-F anti-corrosion type, Y-W outdoor type or Y-WF outdoor anti-corrosion type three-phase asynchronous motors can be selected.
(3) Explosion proof motors, such as YA explosion-proof safety, YB explosion-proof and YF explosion-proof gas filled motors, can be used in places with explosion hazards such as petroleum, chemical industry and coal mines.
2. Selection of voltage and frequency
(1) Selection of voltage. The selection of the rated voltage of the motor depends on the power supply voltage of the power system to the user. The rated line voltage of three-phase asynchronous motor includes 380V, 3kV, 6kV and 10kV. Generally, when the rated power of the motor is less than 220kW, 380V voltage can be used; When the rated power is greater than or equal to 220kW, 6kV.10kV voltage can be used; When the rated power is greater than or equal to 100kW, 3kV voltage can be used.
(2) Frequency selection. The power frequency power supply frequency used in China is 50Hz. If required by the outlet, 60Hz motor can also be selected.
3. Selection of motor power
The motor power need not be too large or too small. If the power is too large, the efficiency of the motor cannot be fully utilized and exerted, which not only increases the purchase cost of the motor, but also makes the efficiency of the motor become very low when it is under light load, and the operation cost is not economical. However, if the power is too small, the motor will overheat, shorten its life, or even burn out if it is overloaded for a long time.
The motor power can be calculated as follows:
Ne= Ke●Nsh (kW)
Where, Nsh ----- shaft power of blower, kW;
Ne -------- Motor power, kW;
Ke -------- Margin coefficient, Ke=1.05~1.25. When mechanical seal and packing seal are used, the larger value shall be taken.
The power Ne obtained from the formula is the power that the motor should have. In fact, the rated power of the motor is graded according to the standard and cannot be selected arbitrarily. If the calculated power Ne is not consistent with the rated power of the motor, the motor must be selected closer to the upper power level.
4. Selection of motor speed
The selection of motor speed is closely related to the blower speed and transmission mode. ① When the direct coupled drive is adopted, the blower and the motor run synchronously, and there is little choice of motor speed. ② For the belt coupled drive, when the motor power is constant, the lower the speed, the larger the size, the more expensive the price, and the lower the efficiency. Therefore, most blowers use deceleration drive.
5. Selection of motor protection grade
The motor enclosure protection types include IP23, IP44 and IP54.
Motor enclosure protection type diagram
Selection steps of Roots blower:
1. List conditions and requirements
(1) Purpose: the position and function of the blower in the process to distinguish the blowing purpose from the vacuum purpose.
(2) Gas property: name, molecular weight, non-toxic, corrosive and explosive, composition ratio of mixed gas, dust content, etc.
(3) Working condition parameters: inlet air temperature, inlet air pressure, pressure rise (exhaust pressure or vacuum degree), flow, and allowable limits for exhaust temperature and noise.
(4) Environmental conditions: installation site (outdoor or indoor, on the ground or floor), local atmospheric pressure, temperature and humidity, etc.
(5) Public conditions: water supply, power supply (including power supply voltage), etc.
(6) Others: ① Off design operation: pressure or flow regulation requirements; ② Operation condition: continuous operation time, or intermittent operation frequency; ③ Requirements for painting (including color), packaging, transportation, etc.
2. Model selection calculation
(1) According to the use requirements, select the material and seal type of the blower, and preliminarily select the product model and specification.
(2) Calculate the performance parameters of the primary products under the specified working conditions, including flow, shaft power, exhaust temperature, etc.
(3) After selecting the model and specification of the blower, determine the prime mover (motor) and transmission mode, and select supporting accessories.
3. List model selection
(1) Blower: ① Model: diameter, material and sealing type; ② Performance parameters: flow, pressure rise (or vacuum degree), speed and shaft power, etc.
(2) Motor: voltage, power, number of poles (or speed), protection grade and insulation grade, etc.
(3) Transmission mode: direct connection, belt connection (whether it is anti-static belt), or other transmission modes.
(4) Supporting accessories: models and specifications of muffler, filter, elastic joint, safety valve, check valve, acoustic enclosure, starting cabinet, etc.
The above is the introduction of the selection method of Roots blower. It's not easy to sort out so many things first. Please pay more attention and praise. Next time, we will introduce the selection calculation of Roots blower in terms of mixed gas transmission. thank you!