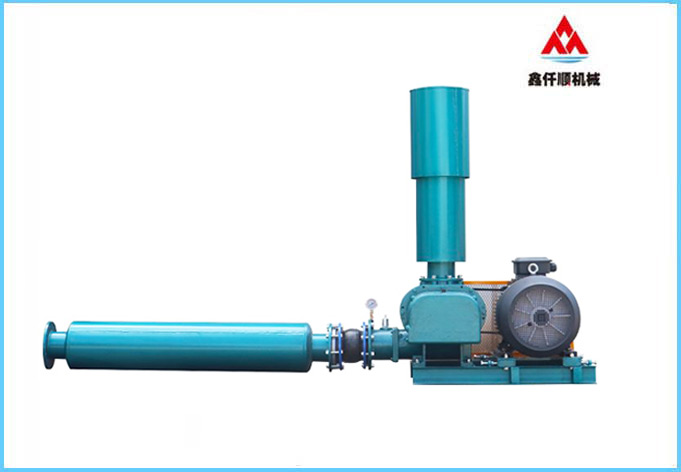
Introduction to selection method of Roots blower?
Source: Roots blower manufacturer
Published on: January 13, 2024
Hits:
Related information
-
Application of Roots blower in sewage treatment -
Roots blower should be properly and timely maintained -
The quality of three blade roots blower is really important -
Introduction to the effect of three blade roots blower on energy saving and emission reduction in wood drying process -
Introduction to the important role of three blade roots blower in laser cutting -
Biogas explosion-proof roots blower: help environmental protection and innovate energy utilization -
What are the causes of tripping of Roots blower frequency converter? -
How to determine the exhaust pressure and water depth of Roots blower? -
What are the requirements of Roots blower for motor? -
Influence of Roots blower and introduction to cooling and maintenance in winter
Xinqianshun's latest products
Random articles
-
How to cool if the outlet temperature of Roots blower is too high? -
Common faults and solutions of Roots blower _ Roots blower -
How much can the pressure of roots blower reach by increasing the pressure of roots blower? -
Introduction to common faults and maintenance of Roots blower -
What are the advantages of CNC planing technology of Roots blower? -
How to configure the motor power of sewage aeration roots blower? How to choose? -
What is the importance of Roots blower? -
How to calculate the air volume of Roots blower in the aeration tank of WWTP? -
What is the role of Roots blower in WWTP? -
Briefly introduce the maintenance of high-pressure water-cooled roots blower (water cooling cycle):
Latest news articles
-
Sharing of application skills of Roots blower in pharmaceutical industry -
Application value of Roots blower in metallurgical industry -
Prospects for the application of Roots blower in coal processing? -
Innovative application of Roots blower in printing and packaging equipment -
High efficiency operation skills of Roots blower in refrigeration system of cold storage -
Introduction to the operation principle of Roots blower in pharmaceutical cleaning equipment -
Application of Roots blower in sewage treatment -
What should be paid attention to when using Roots blower to transport hydrogen? -
Roots blower should be properly and timely maintained -
Roots blower is a common environmental protection equipment in sewage treatment