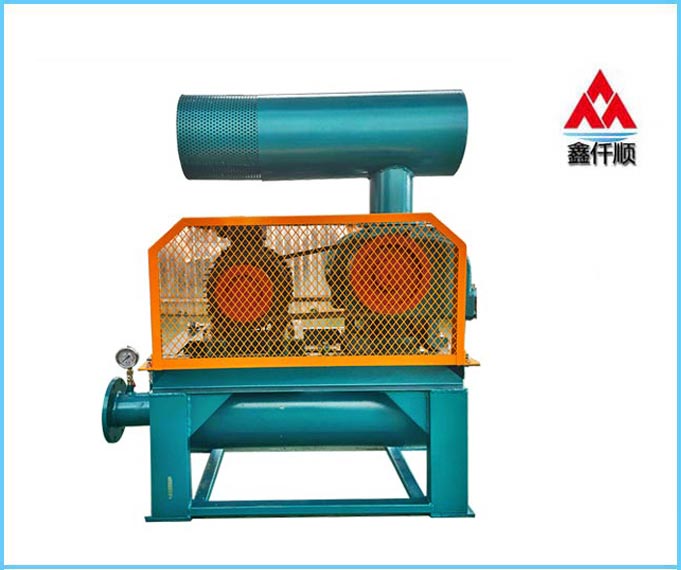
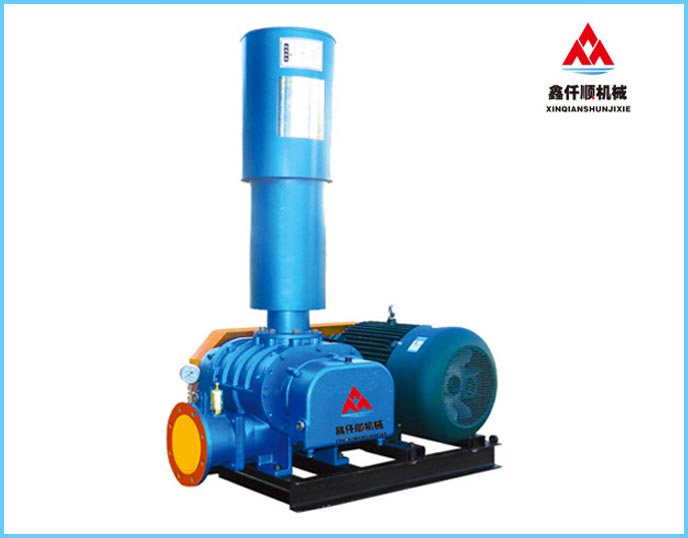
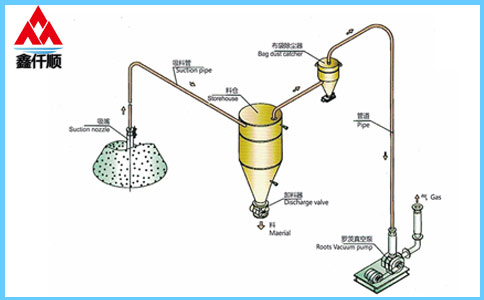
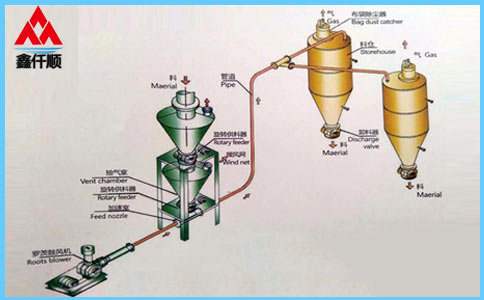
At present, most roots blowers in the market are of three blade type, and two sets of three blade impellers complete the suction and exhaust for three times every revolution of the three blade roots blower. It belongs to positive displacement fan and is a fixed volume rotary pneumatic machinery. The cylinder is contained by the casing and the wall plates at both ends. A pair of mutually "occluding" impellers (because of the gap, the two impellers do not contact directly) separate the air inlet from the exhaust port. Through the rotation of a pair of synchronous gears, the two impellers rotate in the cylinder at the same speed direction. During the rotation, the gas at the air inlet is constantly pushed to the exhaust port by the impeller, So as to achieve the purpose of forced exhaust. Simple structure and stable performance.
Its characteristic is that within the maximum design pressure range, when the resistance of the pipe network changes, the flow changes very little. The pressure change of Roots blower has little influence. When the liquid level in the aeration tank changes, the air blowing volume basically remains unchanged. The air volume of roots blower is controlled by the speed, and the air volume can be adjusted by frequency conversion. The air pressure can be maintained after frequency conversion.
When selecting the blower for the sewage treatment plant, the performance parameters given on the Roots blower manufacturer's product samples are all under the standard air intake state. However, the blower is not under the standard state in actual use. When the environmental conditions of the blower, such as temperature, atmospheric pressure and altitude, are different, the performance of the blower will also change, The performance parameters on the product sample cannot be directly used in the design of model selection, but the performance requirements of the fan need to be converted into the fan parameters under the standard air inlet state according to the actual use state.
The exhaust pressure of the positive displacement blower does not depend on the blower itself, but on the device after the blower is discharged, that is, the so-called "back pressure". The aeration blower has the characteristics of forced gas transmission. The exhaust pressure marked on the blower nameplate is the rated exhaust pressure of the blower. In fact, the blower can work at any pressure lower than the rated exhaust pressure, and can also work above the rated exhaust pressure as long as the strength and exhaust temperature allow.
For the sewage treatment plant, the absolute pressure (back pressure) generated by the exhaust system is the sum of the pressure loss value of the pipeline system, the depth of the aeration tank and the ambient atmospheric pressure. (roughly the water depth plus one meter)
When calculating the oxygen demand for sewage treatment, the result is the mass flow qm (kg/min) of oxygen required under the standard state, and then convert it into the volume flow qv1 (m3/min) of air required under the standard state. If the use state of the blower is not the standard state, such as in the plateau area, the air density and moisture content will change, The volume flow of air supplied by the blower is the same as the standard state, but the mass flow of air supplied will be reduced, which may lead to insufficient oxygen supply. The simplest calculation method is to calculate one square four aeration heads according to the area of sewage pool, and the air supply capacity of each aeration head is 0.03m3/min (0.03 here is the middle value of the aeration head)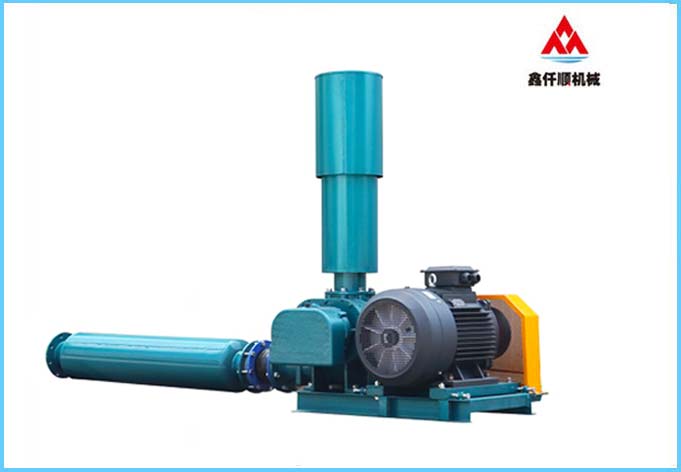
Blower selection shall pay attention to the change rule of air supply flow of the blower. For the same blower, the volume flow will not change in winter and summer, but the mass flow will change due to different air density, that is, the oxygen supply will be different. This is because the temperature in winter decreases and the air density increases, so the mass flow of dry air supplied by the fan increases significantly compared with the standard state, resulting in an increase in the oxygen supply. From the actual measurement of operation, the dissolved oxygen in the aeration tank in winter is 1~3mg/L higher than that in summer every year.
First of all, do not be in a hurry to disassemble the fan, and conduct a comprehensive inspection of the fan. Touch the bearing shells and front and rear machine shells with hands to see if the temperature is normal. Turn the coupling with hands or tools to check whether the fan rotates flexibly. If the temperature is normal everywhere, but the turning gear is sometimes light and heavy, and there is a "bad" phenomenon, it can be determined that the two rotors collide. If the upper casing is opened, collision marks will be observed on the rotor surface. If the surface of one side of the rotor is bright and pitted.
The causes of friction and collision between two rotors are: ① loose gear keyway and key fit; ② The fastening nut at the gear shaft end is loose or the gasket is invalid; ③ The gear hub hole and the main shaft are poorly matched; ④ The bearing clearance exceeds the specified technical requirements; ⑤ The backlash of the gear pair is too large; ⑥ The rotor key is loose.
Practice has proved that the loose fit between the gear keyway and the key on the driving shaft is the main reason for the collision between the two rotors. Further analysis shows that the working surface (two sides) of the key and the two sides of the shaft and the hub keyway are in close contact. These two contact surfaces are interference fit, and the torque of the rotor is transmitted by these two mating surfaces. Due to the large force on the key when the fan is started and the long-term one-way force during operation, the key or keyway is worn, which makes the fitting angle of the two transmission gears deviate and causes the rotor assembly clearance to change, resulting in collision.
At this time, remove the gearbox housing, knock the hexagon fastening nut at the gear end with a hammer, and observe whether it is loose and whether the retaining gasket is invalid. Then, use the impact method to check whether the gear hub and key on the driving shaft are loose. This method is to place a piece of hardwood between the two rotors at the place with the minimum clearance, and rotate the coupling with hands or tools to make the two rotors collide with the hardwood. When striking, observe whether there is relative movement between the gear and the shaft. After impact, re measure the clearance here with a feeler gauge. If there is relative movement between the gear and the shaft during the impact, and the clearance between the two rotors changes after the impact, it can be determined that the hub and key of the driving gear are loose. In this way, the collision between the two rotors can be eliminated by replacing the new key. The repair time is only 2h, which improves the operation rate of Roots blower.
I believe that after reading the above contents, you should also understand the maintenance skills of Roots blower. I hope it will help you.
Text term label: Roots blower
Link to this article: //wuhanzhcs.com/html/news/n02/694.html